Dna Replication Model Ligase | The activated amp residue of the dna ligase/adenylate intermediate is. Dna replication always starts from specific locations which are called as origins of replication. Dna replication requires the activity of dna polymerase, as well as other enzymes such as primase and ligase. Dna ligases catalyse the crucial step of joining breaks in duplex dna during dna repair, replication and. The fragments are then sealed together by an enzyme called ligase.
Semiconservative model of dna replication.dna replication is semiconservative. Dna replication is the process by which a cell makes an identical copy of its dna. A deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base. The three suggested models of dna replication. Dna ligase seals the gaps between the okazaki fragments.
This is the currently selected item. Ligase joins two dna molecules. Dna replication is the process by which a cell makes an identical copy of its dna. Library catalog > dna replication and central dogma. There are more than one origins of replication present on single dna molecule. Helicase primase dna polymerase ligase. Dna ligase seals the gaps between the okazaki fragments. Therefore, dna replication requires that the dna is loosened and the double helix is unwound. This scrollable interactive provides an overview of dna replication and the key enzymes involved, highlighting the role of dna ligase. The lagging strand is therefore synthesised in fragments. Deoxyribonucleic acid, commonly known as dna, is a nucleic acid that has three main components: Dna replication in the model organism e. The final replication product does not have any nicks because dna ligase forms a covalent phosphodiester linkage between 3'.
Semiconservative model of dna replication.dna replication is semiconservative. Suggested models of dna replication : Dna ligase iii and dna ligase iv carry out genetically distinct forms of end joining in human somatic cells. negative regulation of mitochondrial dna replication source: This is the cooper and helmstetter model A deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base.
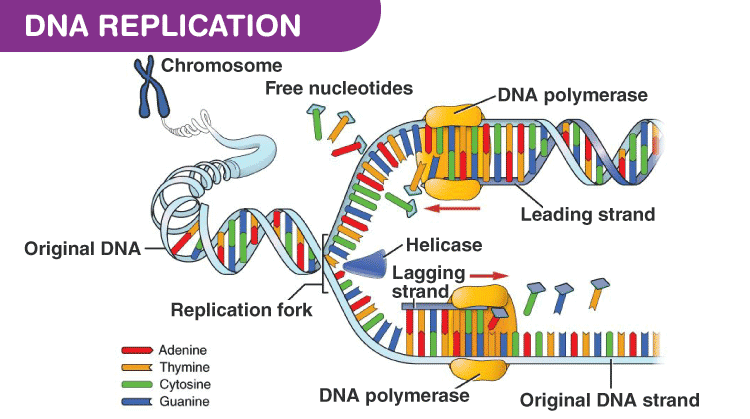
Human dna ligases in replication and repair. This happens because dna polymerases can only read the dna template from the 5' to the 3' end and add free. A deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base. Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell divides, the two new daughter cells must contain the same genetic information, or dna, like the parent cell. Coli has been extensively studied, providing a foundation for understanding the diverse mechanisms of genome figure 9.9 dna ligase reaction. Topoisomerase i nicks dna, relieving torsional tension of the replicating helix. Vaccinia virus dna ligase and chlorella virus dna. The dna ligase catalyzes the formation of covalent phosphodiester linkages, which permanently join the nucleotides together. The lagging strand is therefore synthesised in fragments. Semiconservative model of dna replication.dna replication is semiconservative. There are more than one origins of replication present on single dna molecule. The fragments are then sealed together by an enzyme called ligase. The three suggested models of dna replication.
Dna replication always starts from specific locations which are called as origins of replication. The activated amp residue of the dna ligase/adenylate intermediate is. A deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base. There are more than one origins of replication present on single dna molecule. Dna replication requires the activity of dna polymerase, as well as other enzymes such as primase and ligase.
Suggested models of dna replication : Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell divides, the two new daughter cells must contain the same genetic information, or dna, like the parent cell. Restriction enzymes & dna ligase. This is the cooper and helmstetter model Deoxyribonucleic acid, commonly known as dna, is a nucleic acid that has three main components: The fragments are then sealed together by an enzyme called ligase. Dna replication requires the activity of dna polymerase, as well as other enzymes such as primase and ligase. A disproved model of dna synthesis suggesting more or less random interspersion of parental and new segments in daughter dna molecules. The lagging strand is therefore synthesised in fragments. Topoisomerase ii introduces the double strand break to avoid dna. This leads to the formation of two. The final replication product does not have any nicks because dna ligase forms a covalent phosphodiester linkage between 3'. When dna is replicated, what happens to the old (parent) strands and the new (daughter) strands?
This scrollable interactive provides an overview of dna replication and the key enzymes involved, highlighting the role of dna ligase ligase dna replication. There are more than one origins of replication present on single dna molecule.
Dna Replication Model Ligase: When dna is replicated, what happens to the old (parent) strands and the new (daughter) strands?
Post a Comment